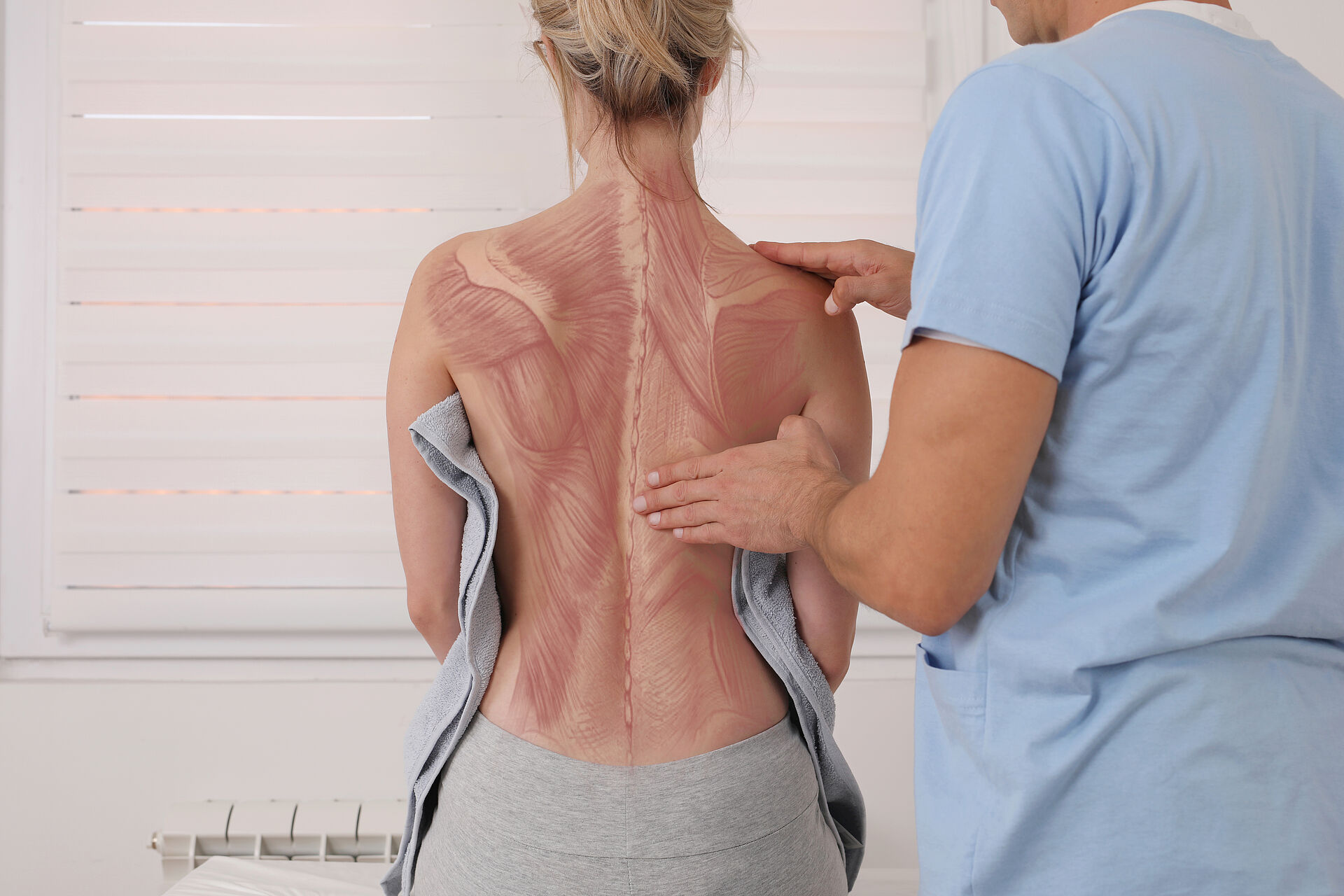
Mobility deficits with consequences
In the human body, the pelvic girdle, trunk and spine, with their complex pathologies, bear a special burden. Particularly in industrialised countries, but also in the developing world, a lack of mobility leads to both economic and individual problems.
- The most frequent indication for physiotherapy in 2012 was pathologies connected to the spine: 42.1% of referrals in Germany were related to pelvic girdle and back pain.
Source: www.statista.com: Statista GmbH, Hamburg. 2014
- A further example: the single year frequency of LBP for employees is from 34% to 51%, while the incidence is 23%.
Source: Statista GmbH, Hamburg: A. Vleeming; Fitzgerald, C.; e. A.: 8. Interdisziplinärer Weltkongress über Schmerzen im unteren Rücken- und Beckenbereich. 2013, 312 - 313
Treatment approaches across the world
In certain countries, the focus on treating pelvic and back pain is a serious concern, above all because of the economic losses when workers are unable to work.
As countries with a very intensive, modern approach to pelvic and spinal rehabilitation, Belgium and Germany must be mentioned side-by-side. Their intense, multi-disciplinary approach places particular emphasis on neuromuscular exercise therapy. Because of the 10-year success of this therapeutic process, patients from 2020 and beyond will return to the workforce thanks to this technique.
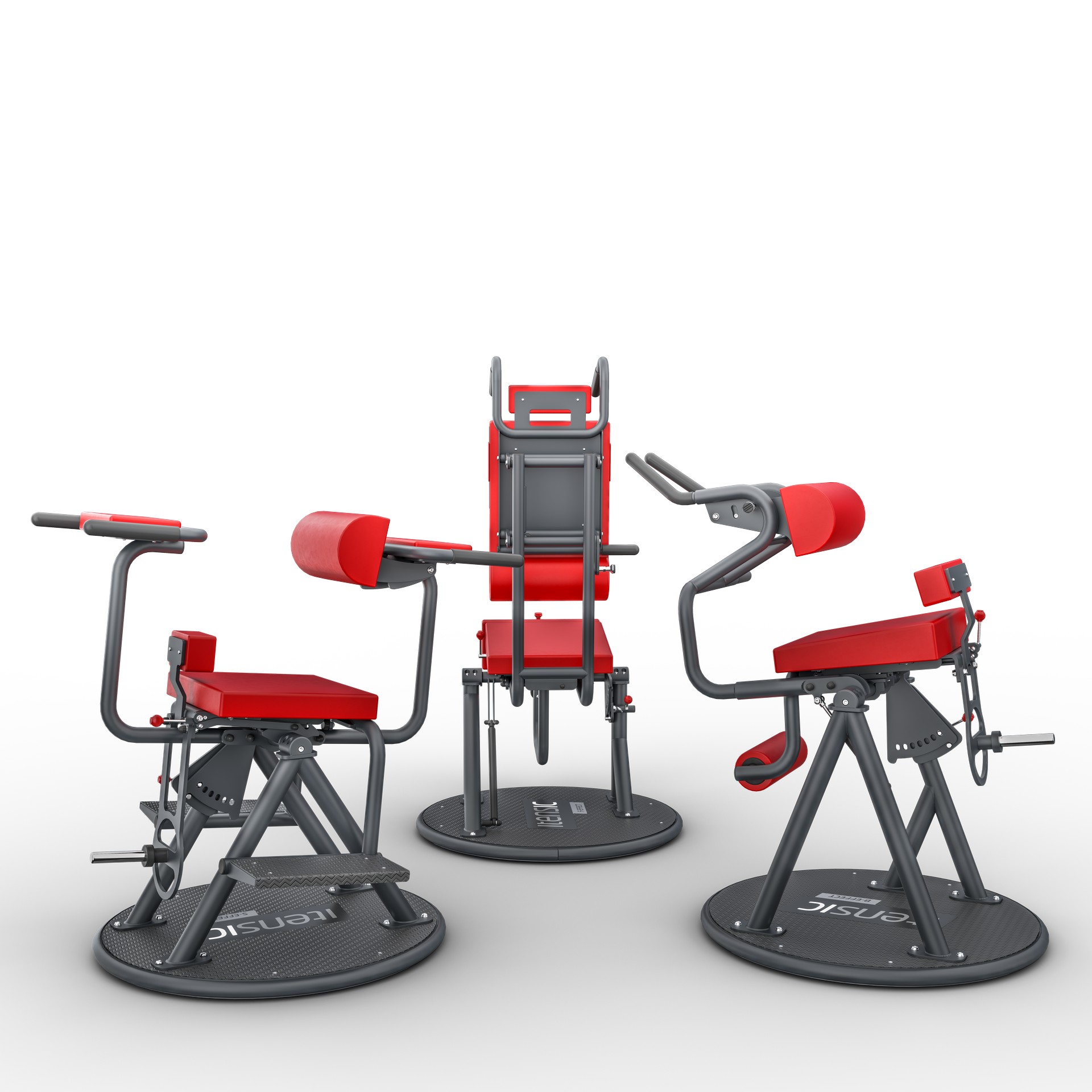
Strength tests are an important part of a rehabilitation process. Patients with different pathologies, ages, genders and training status have to implement neuromuscular diagnostics in order to obtain the basic value for appropriate exercise therapy.
The advantage of isometric and dynamic isotonic tests is to get precise values in a short time in order to plan an individual and appropriate training. The training for the trunk, spine and neck muscles is specific as you are dealing with stabilizers and mobilizers that have different fiber consistencies.
This is not the only reason why it is important to have a controlled training with sinus curves and ultrasound-controlled weight detection that controls the intensity, the time of tension and the subjective interpretation of the effort for progressive resistance training.